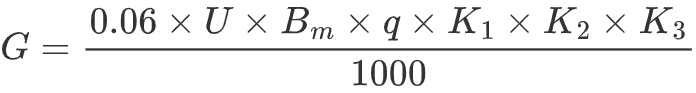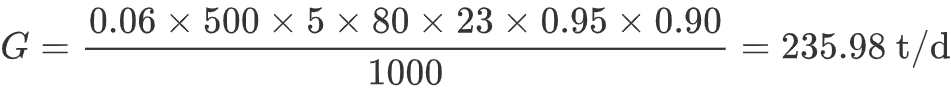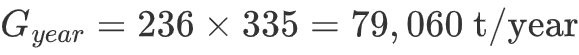Guide to Calculating and Optimizing Paper Machine Production Capacity
The production capacity of a paper machine is a core metric for measuring efficiency, directly impacting a company’s output and economic performance. This article provides a detailed explanation of the calculation formula for paper machine production capacity, the meaning of each parameter, and strategies for optimizing key factors to enhance productivity.
1. Calculation Formula for Paper Machine Production Capacity
The actual production capacity (G) of a paper machine can be calculated using the following formula:
Definitions of Parameters:
- G: Production capacity of the paper machine (tons/day, t/d)
- U: Machine speed (meters/minute, m/min)
- B_m: Web width on the reel (trim width, meters, m)
- q: Basis weight of the paper (grams/square meter, g/m²)
- K_1: Average daily operating hours (typically 22.5–23 hours, accounting for necessary operations like wire cleaning and felt washing)
- K_2: Machine efficiency (ratio of usable paper produced)
- K_3: Finished product yield (ratio of acceptable-quality paper)
Example Calculation: Assume a paper machine with the following parameters:
- Speed U = 500 m/min
- Trim width B_m = 5 m
- Basis weight q = 80 g/m²
- Operating hours K_1 = 23 h
- Machine efficiency K_2 = 95% (0.95)
- Finished product yield K_3 = 90% (0.90)
Substituting into the formula:
Thus, the daily production capacity is approximately 236 tons.
2. Key Factors Affecting Production Capacity
1. Machine Speed (U)
- Impact: Higher speed increases output per unit time.
- Optimization Tips:
- Use high-performance drive systems to reduce mechanical losses.
- Optimize wet-end dewatering to prevent web breaks at high speeds.
2. Trim Width (B_m)
- Impact: Wider web width increases production area per pass.
- Optimization Tips:
- Design the headbox properly to ensure uniform web formation.
- Implement automatic edge control systems to minimize trim waste.
3. Basis Weight (q)
- Impact: Higher basis weight increases paper weight per unit area but may reduce speed.
- Optimization Tips:
- Adjust basis weight based on market demand (e.g., thicker paper for packaging).
- Optimize pulp formulation to enhance fiber bonding.
4. Operating Hours (K_1)
- Impact: Longer production time increases daily output.
- Optimization Tips:
- Use automated cleaning systems for wires and felts to reduce downtime.
- Implement preventive maintenance schedules to minimize unexpected failures.
5. Machine Efficiency (K_2)
- Impact: Low efficiency leads to significant pulp waste.
- Optimization Tips:
- Optimize sheet formation and dewatering to reduce breaks.
- Use high-precision sensors for real-time quality monitoring.
6. Finished Product Yield (K_3)
- Impact: Low yield results in rework or downgraded sales.
- Optimization Tips:
- Improve drying section temperature control to reduce defects (e.g., bubbles, wrinkles).
- Implement strict quality inspection systems (e.g., online defect detection).
3. Annual Production Calculation and Management
1. Annual Production Estimate
Annual production (G_year) can be calculated as:
- T: Effective production days per year
Typically, effective production days are 330–340 days (remaining days are reserved for maintenance).
Continuing the example: Assuming 335 production days/year, the annual output is:
2. Strategies to Increase Annual Production
- Extend equipment lifespan: Regularly replace wear-prone parts (e.g., felts, doctor blades).
- Smart production scheduling: Use big data to optimize production cycles.
- Energy optimization: Install waste heat recovery systems to reduce downtime energy loss.
Conclusion
Understanding the calculation of paper machine production capacity and continuously optimizing key parameters can significantly enhance efficiency and profitability.
For further discussions on paper production optimization , feel free to consult!
Post time: Jul-01-2025